Every great web application starts not with code, but with a solid plan. Building a web app involves four big phases: sketching out your idea, picking your tech, designing the experience, and then actually building the thing. This is the journey from a concept scribbled on a napkin to a real, working product.
Your Blueprint From Idea to Actionable Plan

Before anyone writes a single line of code, the success of your web app is pretty much decided by the quality of its blueprint. This is where you translate a great idea into a concrete, actionable strategy. It’s a step people love to skip, but rushing past it is a classic mistake that leads to wasted money, blown deadlines, and a product nobody really wants.
Think of this plan as your north star. It’s what will guide every technical and design decision from here on out. It makes sure everyone—from developers to stakeholders—is on the same page and working toward the same goals.
Defining Your Core Purpose and Audience
First thing's first: you need to nail down your core idea. What specific problem does your application solve? And who are you solving it for? Getting crystal clear on these two questions is non-negotiable.
For example, "build a fitness app" is way too vague. A much better, more focused goal is "build a web app that provides customized 30-minute workout plans for busy professionals who can't get to a gym." That kind of precision immediately helps you picture your ideal user.
To really understand that user, you need to create user personas—basically, fictional profiles of your target audience. Dig into their:
- Demographics: Age, location, job, and income.
- Goals: What are they trying to accomplish by using your app?
- Pain Points: What frustrations are you trying to fix for them?
- Technical Proficiency: Are they tech-savvy or easily intimidated by new software?
This isn't just a busywork exercise. It ensures you’re building something for real people with real needs, not just a cool piece of tech.
Conducting Thorough Market and Competitor Analysis
Once your purpose is clear, it's time to scope out the market. You need to see if similar products are already out there and, more importantly, if people are actually willing to pay for a solution. The number one reason startups fail is a lack of product-market fit.
Start by searching for direct and indirect competitors. If you find one, don't get discouraged—it's actually a good sign that a market exists. Your job is to find a unique angle or simply do it better. Dive into their strengths, weaknesses, and customer reviews to find the gaps you can fill.
A strong blueprint doesn't just list features. It defines why your app needs to exist in a crowded market. This strategic foundation is your best defense against scope creep and keeps the team focused on delivering real value.
To get your vision down into a clear roadmap, check out a guide to concept development from idea to blueprint.
Scoping and Prioritizing for an MVP
It’s incredibly easy to get carried away with adding "just one more feature." The smartest way to launch is with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)—a bare-bones version of your app with just enough functionality to be useful to early adopters. They'll give you the feedback you need to guide future development.
Start by brainstorming every single feature you can imagine for your app. Then, be ruthless and prioritize them using a framework like MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won't-have). Your MVP should only include the "Must-haves" that solve the core problem for your target user.
This approach gets you to market faster and lets you learn from real user data before you sink a ton of time and money into features nobody wants. To dig deeper into this critical stage, check out our detailed guide on MVP development for startups—it lays out the whole roadmap.
Choosing Your Modern Web Development Stack

Alright, you've got your MVP blueprint. Now for the fun part: picking the tools to actually build it. Choosing your technology stack isn't just a nerdy debate for developers; it's a huge strategic decision. It's what determines how fast your app runs, how easily you can add features later, and even who you can hire to work on it.
Think of it as choosing the core materials for a house. Are you building with wood, brick, or steel? Each has its own strengths and requires a different kind of expertise. Your web app's "stack" is a collection of technologies split into three main layers: the front-end, the back-end, and the database. Nail this combo, and you're setting yourself up for success as you learn how to build a web application from scratch.
Understanding the Front-End: What the User Sees
The front-end is everything your users see and click on in their browser. Also called client-side development, this is where you build the user experience—the buttons, the layout, the animations. It’s all about making your app look good and feel intuitive.
Every single website is built on a foundation of three core technologies:
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language): This is the skeleton. It gives your pages their basic structure.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): This is the painter and interior designer, adding all the colors, fonts, and layouts.
- JavaScript (JS): This is what brings the app to life, making it interactive and responsive to what the user does.
While you could technically build a site with just these three, nobody really does that for a complex application anymore. Modern development leans heavily on JavaScript frameworks like React, Vue.js, and Angular. These tools provide reusable components and a structured approach that makes building sophisticated interfaces much faster and more manageable.
Pro Tip: React, originally built by Meta, is the undisputed king right now. Its component-based approach is powerful, and the massive community means you'll never have trouble finding developers or answers. On the other hand, Vue.js is often praised for its simplicity and gentle learning curve, making it a fantastic choice for smaller teams that need to move quickly.
Powering the Application: The Back-End Engine
If the front-end is the car's interior, the back-end is the engine. This is the server-side part of your app that users never see, but it does all the heavy lifting. It handles things like user authentication, business logic, and talking to the database.
When someone clicks "Save" on their profile, that request zips over to the back-end. The back-end code processes it, updates the database, and sends a "success" message back to the front-end. It’s the brains of the whole operation.
A few popular choices for the back-end include:
- Node.js with Express: This is a huge one because it uses JavaScript. That means your developers can use the same language on both the front-end and back-end, which is incredibly efficient. It’s perfect for real-time applications like chat bots or live dashboards.
- Python with Django or Flask: Python is famous for its clean, readable code and massive library ecosystem. This makes it a go-to for anything involving data science or machine learning. Django is the "batteries-included" framework with everything you need, while Flask is more of a lightweight, build-your-own-adventure option.
- Ruby on Rails: Rails is all about developer productivity. Its "convention over configuration" philosophy means you can build things incredibly fast, especially in the early stages.
Making this call is a big deal. For a much deeper look, we've put together a full guide on how to choose a tech stack that breaks down the pros and cons even further.
Comparing Popular Web Development Tech Stacks
To make sense of it all, it helps to see how these technologies bundle together into popular "stacks." Each stack has its own personality and is suited for different kinds of projects. Here’s a quick comparison to help you see where your project might fit.
| Stack | Core Technologies | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| MERN | MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js | Single-page applications, real-time apps, projects needing high flexibility. | Uses JavaScript across the entire stack, simplifying development and hiring. |
| LAMP | Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP | Content management systems (like WordPress), e-commerce, traditional websites. | Proven, stable, and supported by a massive open-source community. |
| Ruby on Rails | Ruby, Rails framework, database of choice | Rapid prototyping, startups, MVPs, complex web applications. | Convention over configuration enables extremely fast initial development. |
Each of these has powered countless successful applications, so there's often no single "right" answer. The best choice depends entirely on your project's specific needs, your team's skills, and your long-term goals.
Selecting the Right Database
Your database is the long-term memory for your application. It’s where every piece of data lives, from user accounts and passwords to product inventories and order histories. Your choice here boils down to two main camps: SQL and NoSQL.
SQL (Relational) Databases, like PostgreSQL and MySQL, are the traditional choice. They store data in neat, organized tables, much like a collection of linked spreadsheets. This structure is perfect for applications where the data relationships are clear and consistent—think of an e-commerce store with its users, products, and orders.
NoSQL (Non-Relational) Databases, like MongoDB and Firebase, are more flexible. They often store data in JSON-like documents, which means you don't need a rigid structure upfront. This makes them a great fit for projects with evolving data needs, like a social media app or an IoT platform where the data you collect might change over time.
This decision is about more than just technology; it’s about development speed. In fact, the global low-code development platform market is projected to skyrocket to USD 187 billion by 2030, a massive leap from USD 10.3 billion in 2019. This explosion shows a clear demand for tools that make complex tasks, like database management, way simpler.
5. Designing an Experience People Will Actually Use
Once your tech stack is sorted out, it's time to shift your focus from the engine to the cockpit—the part of your application users will see, touch, and interact with every day. A lightning-fast back-end is completely wasted if the front-end is confusing, ugly, or just plain frustrating. This is where User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) design move from being buzzwords to the single most important factor in your project's success.
A lot of people throw "UI" and "UX" around like they're the same thing, but they are two very different disciplines that absolutely have to work in harmony. Think of it like a house: UX is the architectural blueprint. It dictates how the rooms flow together, where the doors and windows go, and how easy it is to live in the space. UI, on the other hand, is the interior design—the paint colors, the furniture, the light fixtures that make the space look and feel great.
Getting UI and UX Right
A great user experience feels invisible. UX design is all about making your application logical, intuitive, and even enjoyable to use. It’s about deeply understanding what a user wants to achieve and then ruthlessly cutting away any friction that stands in their way. A UX designer is constantly asking, "What's the user's goal on this screen?" and "What's the absolute simplest path to get them there?"
UI design is purely about the visuals. It’s the craft of creating the application's look and feel, zeroing in on things like color palettes, typography, button styles, and spacing. Good UI guides the user's eye with a clear visual hierarchy and establishes a consistent brand identity. It takes that functional UX blueprint and translates it into an interface that’s both attractive and easy to navigate.
You absolutely need both to succeed.
Great UX with poor UI is like a well-designed car with a terrible paint job—it works perfectly, but nobody really wants to be seen in it. On the flip side, great UI with poor UX is a beautiful car with the steering wheel in the back seat. It looks incredible but is completely useless.
From a Napkin Sketch to an Interactive Blueprint
Before a single line of front-end code gets written, you have to visualize the app's layout and user flow. This process always starts with wireframes and then moves on to mockups. These are the essential blueprints for your app's screens.
Wireframing is the first, low-fidelity step. It’s a basic, black-and-white sketch of your app's structure, focused entirely on layout and where content will live. You can literally do this with a pen and paper or jump into a digital tool. The goal isn't to make it pretty; it's to force everyone to think about functionality and information hierarchy before getting distracted by colors and fonts.
After the wireframes are locked in, the process moves to mockups. Mockups are high-fidelity, full-color designs that show exactly what the final product will look like. They bring in the branding, typography, imagery, and all the polished UI elements. This is where the UI designer really shines, turning the spartan wireframe into a pixel-perfect representation of the final application.
These visual guides are the source of truth for your developers. They eliminate guesswork and ensure the product that gets built is the product that was designed.
If you're new to this part of the process, our guide on how to create wireframes is the perfect place to start mapping out your application's structure.
Responsive Design Isn't a Feature, It's a Requirement
These days, people will access your application from a wild variety of devices—massive desktop monitors, laptops, tablets, and every smartphone size imaginable. A responsive design ensures your application looks and works perfectly on every single one of them. With over 60% of all website traffic now coming from mobile devices, building for mobile isn't just a good idea; it's a basic requirement for survival.
Responsive design uses flexible layouts and CSS to automatically adapt to the user's screen size. In practice, this means:
- A layout with multiple columns on a desktop might stack neatly into a single column on a phone.
- Complex navigation menus often collapse into a "hamburger" icon on smaller screens.
- Buttons and text automatically resize to stay legible and easy to tap.
Skipping responsive design will deliver a terrible user experience, tank your SEO rankings, and bleed users. Every design and development decision you make has to be viewed through a "mobile-first" lens from day one.
The Development Lifecycle From Code to Deployment
Alright, you've got a solid plan and you've picked your tech. Now for the fun part: turning that vision into actual, working code. This is where we bridge the gap between a great idea and a real, live product. A modern development process isn't just about hammering out code; it's about building a repeatable, automated system that gets your application built, tested, and into the hands of users reliably.
The first thing you absolutely need is a version control system. Seriously, don't even think about skipping this. Git is the undisputed king here, and for good reason. It lets your team work on different features at the same time without tripping over each other's work. Think of it as a super-detailed history book for your code, tracking every change and making it painless to roll back if something breaks.
Setting Up Your CI/CD Pipeline
Once your code is neatly tucked into a Git repository, the next move is to automate your deployment. This is where Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) come into play. A CI/CD pipeline is basically an automated assembly line that grabs new code, runs a bunch of checks on it, and then pushes it out to your live server.
This kind of automation is a total game-changer. It gets rid of manual, error-prone deployment steps and radically cuts down the time it takes to release new features or fix bugs. Forget about stressful, all-hands-on-deck launch days; you can push updates with a single click.
A basic pipeline usually looks something like this:
- Code Commit: A developer pushes a change to the Git repository.
- Build Trigger: This automatically kicks off a build on a CI server like Jenkins or GitLab CI.
- Test Run: The server runs all your automated tests to make sure the new code didn't break anything.
- Deployment: If the tests all pass, the CD system automatically deploys the code to your hosting environment.
This pipeline creates an incredibly tight feedback loop. If a bug sneaks in, the team knows about it in minutes—not weeks—and can squash it long before a user ever sees it. This is a core principle when you build a web application from scratch that needs both speed and quality.
Implementing a Robust Testing Strategy
No app should see the light of day without being thoroughly tested. Automated testing is your safety net, giving you the confidence to make changes without constantly worrying about breaking existing features. There are really three layers of testing you need to think about.
- Unit Tests: These are small, hyper-focused tests that check individual bits of your code in isolation, like a single function. They're lightning-fast to run and form the foundation of your testing suite.
- Integration Tests: These tests make sure that different parts of your application play nicely together. An integration test might check that when a user submits a form on the front-end, the back-end actually saves the correct data to the database.
- End-to-End (E2E) Tests: These simulate a full user journey from start to finish. An E2E test might automate a user signing up, adding an item to their cart, and checking out, confirming the entire workflow is seamless.
This is the point where the visual blueprint from the design phase gets turned into functional code that's ready for this kind of rigorous testing.
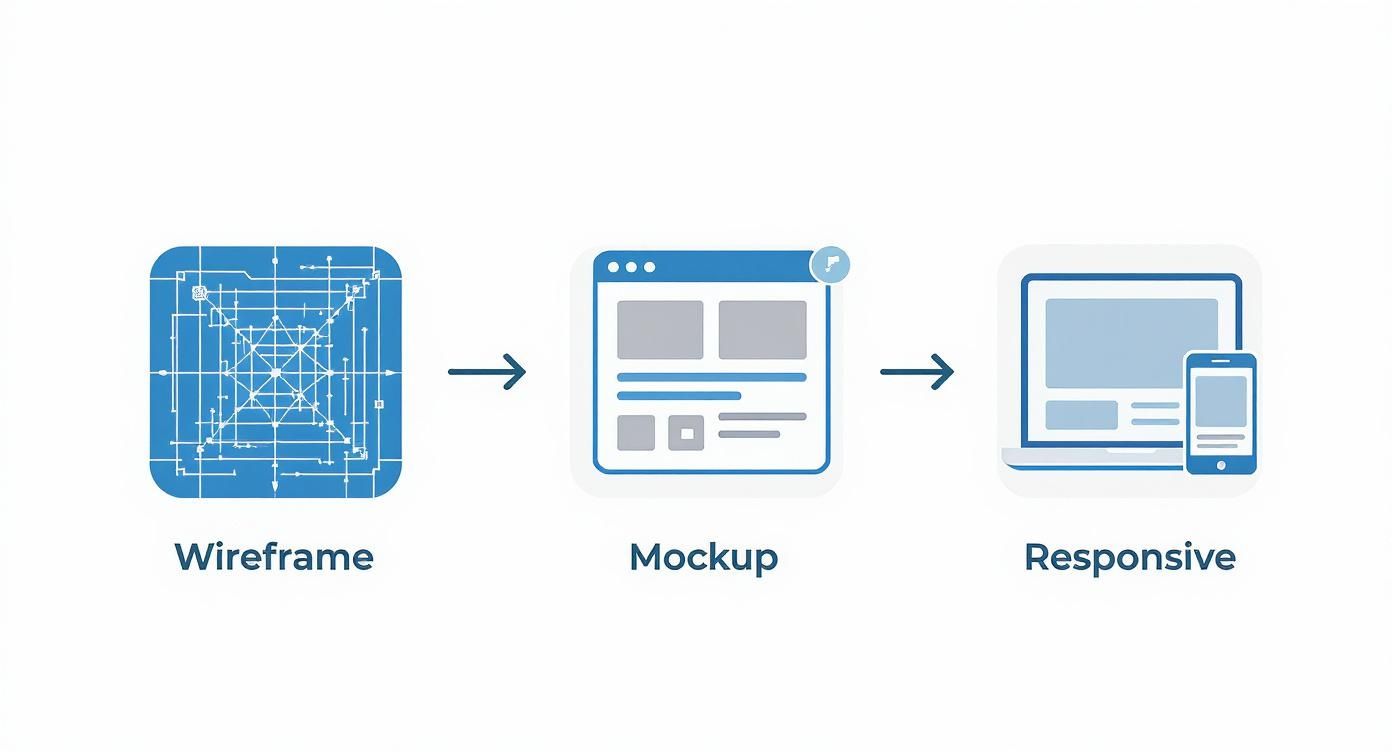
As you can see, a structured plan—from wireframe to mockup to responsive design—gives developers the guide they need to write code that can then be put through the wringer with unit, integration, and E2E tests.
Choosing Your Hosting and Deployment Environment
Finally, your application needs a home on the internet. Your hosting choice is a big deal, and it's all about balancing cost, scalability, and how much server management you're willing to do yourself.
For startups and MVPs, Platform as a Service (PaaS) providers like Heroku or DigitalOcean App Platform are often the perfect starting point. They handle all the server headaches for you, letting you focus entirely on your code. You just push your code, and the platform handles the rest. It's a fantastic way to get moving quickly.
As your app grows and your needs get more complicated, you might outgrow a PaaS and move to an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Google Cloud Platform. These platforms give you total control over your server environment but also come with a much steeper learning curve. The payoff is massive flexibility and the power to fine-tune performance and cost down to the last detail.
Integrating AI for a Smarter Application
Building a functional web application is a massive achievement, but let's be honest—today's users expect more. They're looking for apps that feel intuitive, personal, and frankly, a little bit magical. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) stop being buzzwords and become practical tools for creating a genuinely better user experience.
Integrating AI doesn't mean you have to build a complex neural network from the ground up. Far from it. You can tap into powerful, accessible APIs and pre-trained models to add features that give your app a serious competitive advantage. This is a crucial part of learning how to build a web application from scratch that actually gets noticed.
Powering a Personalized User Experience
One of the quickest ways AI can make an impact is by delivering deeply personalized experiences. The days of one-size-fits-all content are over. AI can analyze user behavior, preferences, and past actions in real-time to tailor the application to each individual.
Think about these real-world examples:
- E-commerce Recommendations: An AI engine can suggest products a user is likely to buy based on their browsing history, past purchases, and what similar users have bought. This is worlds more effective than just showing a "most popular" list.
- Content Platforms: For a news app or blog, AI can curate a personalized feed, surfacing articles and topics that align with a user’s reading habits. The result? They stick around longer.
- Dynamic UI: The app can even adapt its own interface. For instance, an AI might learn which features a specific user accesses most often and bubble them up for easier access in the navigation.
These kinds of features transform a static app into a dynamic, responsive partner that anticipates what the user needs.
Automating Support and Streamlining Operations
Beyond what the user sees, AI is a powerhouse for automating internal processes and making your operations more efficient. One of the most common and effective applications here is the AI-powered chatbot.
Modern chatbots have come a long way from simple, scripted responses. They can understand natural language, securely access user account information, and resolve common issues without ever needing a human. This frees up your support team to tackle the truly complex problems, which dramatically cuts down on wait times and operational costs.
The integration of AI has become a standard practice, not an optional extra. It drives the personalization and automation that users now expect, making it a critical component for modern web applications.
This isn't just a trend; it's a fundamental shift. In fact, 75% of businesses are expected to use AI-driven web technologies, and AI-powered chatbots have been shown to boost customer support efficiency by 60%. You can explore more of these web development statistics to see just how widespread this has become.
Accelerating Development with AI Assistants
AI's role isn't just limited to the final product—it's also reshaping how we build software. AI coding assistants like GitHub Copilot have become indispensable tools for developers everywhere.
These assistants are game-changers. They can:
- Suggest Code Completions: By analyzing the context of your code, they can suggest entire functions or blocks of code, which seriously speeds up the development cycle.
- Generate Boilerplate Code: All those repetitive setup tasks can be automated, letting developers jump straight to the complex business logic that matters.
- Help with Debugging: AI can often spot potential errors or suggest fixes for bugs, saving hours of frustrating troubleshooting.
By offloading routine coding tasks, these tools empower your team to build more robust features, faster. Embracing AI—both within your app and in your workflow—is a powerful strategy for building a smarter, more competitive product.
Your Pre-Launch Checklist and Growth Strategy
Getting to launch day is a huge milestone. After all the work you've put into building your web application from scratch, the urge to just hit "deploy" and pop the champagne is massive. But hold on a second. What you do in these final moments is what separates a smooth release from a chaotic one.
Think of launch day as the start of your app's life, not the finish line. A successful debut depends on a final, tough checklist to make sure everything is polished, secure, and ready for your first users. This isn't just about code; it's about setting up the systems that will fuel your growth from day one.
Final Technical Polish and Security Audits
Before you go live, it’s time for a deep dive into performance and security. Your app might run flawlessly on your development machine, but a live server with real traffic is a completely different animal.
Start with performance tuning. Get into the weeds with your app's load times, how efficiently it queries the database, and how fast the server responds. Even a one-second delay in page load can jack up your bounce rates by over 30%. Use your browser's developer tools and server-side monitoring to find and squash any performance bottlenecks.
Next up, a thorough security audit. This is non-negotiable. Comb through your code and infrastructure for common vulnerabilities like SQL injection or Cross-Site Scripting (XSS). Make sure all sensitive data is encrypted, user authentication is solid, and you have defenses against common attacks. A single security breach can destroy user trust for good.
Setting Up Analytics and SEO Foundations
If you can't measure it, you can't improve it. Before your first user even thinks about signing up, you absolutely must have analytics tools configured and ready to roll. The goal is to understand what people are doing from their very first click.
Here’s your essential setup:
- Google Analytics (GA4): Get that tracking code installed to monitor where traffic is coming from, who your users are, and how they behave on your site.
- Event Tracking: Set up specific events to track the actions that really matter—user sign-ups, feature usage, or successful checkouts.
- Heatmap Tools: Seriously consider tools like Hotjar or Crazy Egg to see exactly where users are clicking, tapping, and scrolling.
While you're at it, lay the groundwork for Search Engine Optimization (SEO). You want your app to be discoverable. Start with on-page SEO basics like optimizing title tags, writing compelling meta descriptions, and making sure your site has a logical URL structure. These first steps are critical for pulling in organic traffic down the road.
A launch without analytics is like flying blind. You're generating valuable data from the moment you go live; failing to capture it means you're throwing away your most important asset for making informed decisions.
Your Post-Launch Growth and Iteration Plan
The second your application is live, the feedback loop kicks into high gear. Your post-launch strategy should be all about systematically collecting that feedback and using it to decide what to build next. Don't just assume you know what users want—let them tell you.
As you get closer to deploying, a well-defined strategy is crucial. You can get a great handle on your next release by following an ultimate 8-step product launch checklist. This will make sure you cover all your bases, from final testing to marketing messages.
The cycle of a healthy, growing application looks like this:
- Gather Feedback: Be proactive. Ask for feedback through surveys, support tickets, and direct user interviews. Pay close attention to bug reports and feature requests.
- Analyze Data: Mix that qualitative feedback with the hard numbers from your analytics. Look for patterns in user behavior that show you where people are getting stuck or which features they love.
- Prioritize Updates: Use what you've learned to build a prioritized roadmap for your next development sprint. Focus on the fixes and features that will deliver the most value to your users.
- Iterate and Deploy: Push updates regularly. A continuous cycle of improvement shows users you're listening and keeps them coming back.
This iterative process is the engine that drives long-term success. It ensures your application doesn't just sit there and become stale. Instead, it evolves based on real-world use, constantly adapting to the needs of a growing user base.
Ready to transform your idea into a high-performance web application? The journey of building a web app from scratch is complex, but you don't have to do it alone. The experts at Up North Media specialize in custom web app development, data-driven SEO, and AI integration to help businesses like yours accelerate growth. Schedule your free consultation today!
