Picking the right tech stack isn't about chasing the "best" new thing. It’s about finding the right fit for what you’re trying to build. This process is all about connecting your business vision to your technical foundation before a single line of code gets written.
1. Ground Your Choices in Business Goals, Not Hype
Jumping straight into a debate over React vs. Vue or Python vs. Node.js is a classic rookie mistake. It's like arguing over which brand of hammer to buy before you’ve decided if you're building a doghouse or a skyscraper.
The most durable, effective tech stacks are a direct reflection of clear business objectives. They aren't built on a developer's personal preference. Before you get lost in the endless sea of options, you have to ground your thinking in three fundamental pillars: the problem you're solving, the user you're building for, and the real-world constraints you're stuck with.
Getting this alignment right from the start is the single most important thing you can do to prevent costly rebuilds and make sure your tech can actually support your growth down the line.
This discovery phase sets the stage for every technical decision that follows. It’s a simple, logical flow that puts business needs firmly in the driver's seat.
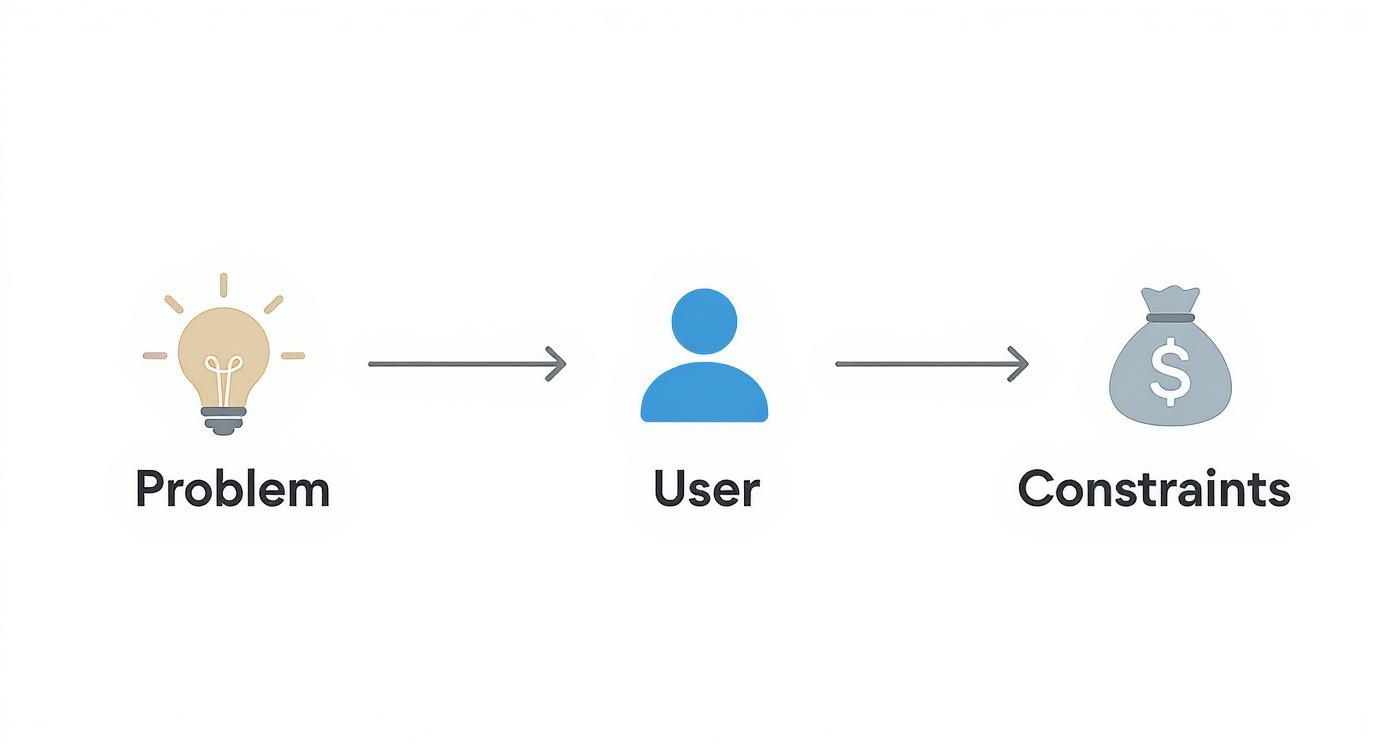
This progression ensures that what you need to build—not the latest shiny tech trend—drives your development forward.
Before digging into frameworks and databases, it helps to summarize the big-picture questions you need to answer.
Core Decision Drivers at a Glance
| Factor | Key Question to Ask | Why It Matters for Your Stack |
|---|---|---|
| Problem & Scope | What, exactly, is this product supposed to do at its core? | Defines complexity. A simple blog has vastly different needs than a real-time trading platform. |
| End-User | Who are we building this for, and how will they use it? | Influences front-end choices, performance needs, and scalability. (e.g., internal B2B tool vs. global consumer app). |
| Constraints | What are our real-world limits on time, budget, and talent? | Dictates technology choices. A tight deadline favors familiar tech; a small budget rules out expensive managed services. |
This table forces you to think strategically first, which makes the tactical decisions about specific technologies much, much easier.
Define the Core Problem and Project Scope
So, what is this application actually supposed to do? Answering this with brutal honesty will immediately clarify your technical needs. Are you building a simple blog, a complex e-commerce site with real-time inventory, or a data-heavy AI application?
- Content-Driven Site: The goal is fast, reliable content delivery. A solid Content Management System (CMS) is key, and the rest of the stack can be pretty straightforward.
- E-commerce Platform: Here, things get serious. You need transactional integrity, secure payment gateway integrations, and rock-solid security. Your backend and database choices are critical.
- AI-Powered App: This demands serious computational power and the ability to chew through massive datasets. An ecosystem like Python’s becomes a natural starting point.
Nailing this down prevents you from over-engineering a simple project or, even worse, under-engineering a complex one. For startups, this means focusing ruthlessly on a core feature set. A great way to frame this is by exploring how to build a Minimum Viable Product, which you can read more about in our guide on MVP development for startups.
Understand Your End-User
Who are you building this for? And how will they interact with it? The answers directly shape your front-end technology and how you plan for scale. A B2B internal tool for a dozen employees on desktops has completely different requirements than a mobile app you hope will serve millions.
You also have to consider the user's technical environment. If your audience is in a region with spotty internet, a lightweight front-end that sips data isn't just a nice-to-have—it's essential. If they expect a highly interactive, real-time experience like Figma, you’ll need a stack that’s great with WebSocket communication.
Your tech stack is just a tool to deliver value to a user. If your choices create friction, slow things down, or don't work on their device, you've picked the wrong stack—no matter how “modern” it is.
Acknowledge Your Constraints
Every project has real-world limits. Ignoring them is a surefire way to fail. The big three constraints are almost always time, budget, and talent.
- Time to Market: Do you need an MVP out the door in three months, or do you have a year-long runway? Frameworks with a steep learning curve are a terrible choice for a rapid launch.
- Budget: This impacts everything from hiring senior developers to choosing managed cloud services over a server you manage yourself. Your stack choices have to fit your financial reality.
- Talent Availability: This one is huge. Can you actually hire people who know this technology? Choosing an obscure but technically elegant language is a dead end if you can't find anyone to build or maintain it.
Picking the Right Architectural Blueprint
Before you even start daydreaming about programming languages or frameworks, you need a high-level plan. This is your project's architectural blueprint. It dictates how every single piece of your application will connect and communicate, and it's a foundational decision that impacts everything from development speed to your ability to scale down the road.

Think of it like building a house. You wouldn't just start buying lumber and windows without knowing if you're building a cozy one-room cabin or a sprawling mansion with a dozen wings. The architecture has to match the scale and complexity of your vision.
Monolithic Architecture: The All-in-One Powerhouse
A monolithic architecture is that cozy cabin—a single, unified unit where every component is interconnected. The entire application, from the user interface to the database logic, is built and deployed as one solid piece. For many projects, especially early-stage startups and MVPs, this is a huge advantage.
Here's when a monolith makes a ton of sense:
- Speed is Everything: You can build and ship features much faster because the entire codebase is in one place. There’s no complex networking to manage between separate services.
- Simple Development: Debugging is often more straightforward. You can trace a request through the entire stack within a single, familiar application.
- Early-Stage Products: When you're still hunting for product-market fit, a monolith’s simplicity lets you iterate and pivot quickly without the headache of managing a distributed system.
A new e-commerce startup is a classic example. A small team can use a monolithic approach to rapidly launch a site with product listings, a shopping cart, and a checkout process all bundled neatly together.
Microservices: The Distributed Specialists
On the flip side, a microservices architecture is like building that sprawling estate with separate, specialized buildings. Each core function—like user authentication, product inventory, or payment processing—is its own small, independent service. These services then talk to each other over a network, usually through APIs.
This approach definitely adds complexity, but it offers incredible flexibility and scalability for large, multifaceted applications. As you design your blueprint, you have to consider effective system integration capabilities to make sure everything operates smoothly across different platforms.
The big idea behind microservices is that each service can be developed, deployed, and scaled on its own. This lets smaller, focused teams own their specific service without disrupting the entire application.
An established e-commerce giant like Amazon is the poster child for this. Their recommendation engine is a completely separate service from the shopping cart, which is separate from the shipping logistics. This allows them to update one tiny part of their massive operation without having to redeploy everything.
Serverless Computing: The On-Demand Model
Serverless is a different beast altogether. Instead of worrying about managing servers—virtual or physical—you deploy your code as individual functions that get triggered by specific events. The cloud provider (like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure) handles all the underlying infrastructure, and you only pay for the exact compute time your functions use.
This event-driven model is a game-changer for apps with unpredictable or "spiky" traffic. Think about a photo-processing app where users upload images sporadically. With a serverless setup, a function to resize an image only runs when an upload happens, costing you absolutely nothing when it's idle.
Ultimately, the right blueprint has to align with your resources and long-term goals. A smart architectural choice doesn't just support your product today; it sets the stage for future growth. In fact, modern, flexible tech stacks can improve query performance by up to 70% and slash the total cost of ownership by about 50%. By carefully weighing these architectural patterns, you can make an informed choice that truly supports your project’s unique demands.
Choosing Your Languages and Frameworks
Once your architectural blueprint is solid, it's time to pick the actual materials—the programming languages, frameworks, and runtimes that will bring your project to life. This isn't about chasing whatever's hot on Hacker News. It's about finding a stable, productive, and maintainable foundation that fits your specific needs. The goal is to choose a powerful ecosystem, not just a popular tool.
Honestly, this is a critical fork in the road. The language or framework you commit to will influence everything from who you can hire to how easily you can add features a few years from now. It’s a long-term relationship, so choose wisely.
Look at the Ecosystem, Not Just the Language
It's easy to get bogged down in endless "Language A vs. Language B" debates online. A far more productive approach is to evaluate the entire ecosystem around a technology. A strong ecosystem offers a lot more than just a compiler; it’s a support network that speeds up development and cuts down on risk.
When you're sizing up an ecosystem, here's what to look for:
- Community Support: How active is the community? When your team hits a wall at 2 AM, a vibrant community on platforms like Stack Overflow or GitHub means someone, somewhere, has probably already solved your problem.
- Documentation Quality: Is the official documentation clear, thorough, and up-to-date? Bad documentation can grind development to a halt and lead to some seriously expensive mistakes.
- Maturity and Stability: New tech is exciting, but mature frameworks that have been battle-tested in production environments offer stability and a predictable road ahead. For mission-critical apps, this is non-negotiable.
- Available Libraries and Tools: A rich ecosystem comes with a treasure trove of third-party libraries that solve common problems, saving your team from reinventing the wheel for things like authentication or image processing.
Take the JavaScript ecosystem, for example. With Node.js on the backend and frameworks like React or Vue on the front end, it's absolutely massive. This is why JavaScript-based stacks like MERN and MEAN are so dominant. Globally, over 500,000 developers use these frameworks, and startups that adopt them can potentially slash their time-to-market by around 40%. You can explore more data on how tech stacks influence business outcomes to get a better sense of the numbers.
The Classic Tradeoff: Performance vs. Developer Speed
Here's one of the central dilemmas you'll face: raw performance versus how fast your team can actually build and ship code. Sure, a language like Rust or Go might give you blistering performance for a high-frequency trading algorithm, but the learning curve and development time could be way higher than with Python or Ruby.
For most web applications, developer productivity is frankly the more important metric. A framework like Ruby on Rails or Python's Django lets a small team build complex, feature-rich applications incredibly fast because they handle so much of the boilerplate code for you.
Your decision should be guided by your project's real bottlenecks. If your app's success hinges on processing millions of requests per second, performance is king. If it relies on shipping new features to users every week, then you need to prioritize development speed.
Think of it this way: a Formula 1 car is built for pure speed, but it requires a pit crew of specialists to maintain. A reliable sedan gets you where you need to go with far less hassle. Choose the vehicle that actually fits the journey you're on.
The Ultimate Reality Check: Can You Hire for It?
This might be the most practical consideration of all. Can you actually find and afford developers who are good at the technology you choose? A technically "perfect" stack is completely useless if you can't hire anyone to build or maintain it.
This is where popular, well-established technologies have a huge advantage. There are simply far more JavaScript and Python developers out there than for niche languages like Elixir or Haskell. This has a direct impact on both your hiring timeline and your budget.
For instance, the massive demand for Python in AI and data science means salaries can range from $75,000 to over $200,000, depending on experience. Understanding these market dynamics is essential. Before you commit, do some research on local and remote talent markets to make sure your chosen stack is a sustainable investment for your team and your bottom line.
Selecting Your Database and Hosting Environment
Your data is the lifeblood of your app. Where you decide to store it and how you run your application are choices with seriously long-term consequences.
These decisions directly hit your app's performance, how easily you can scale up when things take off, and what your monthly bills will look like. It all boils down to two key questions: how will you structure all that data, and where is your application actually going to live?
This isn't about finding the single "best" technology out there. It’s about picking the one that truly fits your application's specific needs. The conversation usually starts with the great database debate: SQL vs. NoSQL.
SQL vs. NoSQL: The Great Database Debate
Think of choosing a database like deciding between a perfectly organized filing cabinet and a set of super-flexible storage bins. One is built for structure and predictability, while the other is all about handling a messy, evolving collection of items.
SQL databases (think PostgreSQL or MySQL) are the filing cabinets. They use a rigid schema with tables, rows, and columns. Everything is highly organized, and the relationships between different pieces of data are locked in.
This structure is perfect for apps where data integrity and complex, multi-step transactions are non-negotiable.
- E-commerce platforms are a classic example. When a customer buys something, you need to update inventory, process the payment, and create a shipping record all at once. SQL ensures this whole transaction either succeeds completely or fails completely, preventing corrupted data.
- Financial apps are another perfect fit. Consistency is everything. SQL’s strict structure guarantees that every financial record is accurate and reliable.
NoSQL databases (like MongoDB or Cassandra) are your flexible storage bins. They don't demand a fixed schema and can store data in all sorts of formats—documents, key-value pairs, you name it. This makes them incredibly adaptable.
- Social media feeds thrive on this. A user's profile might contain text, images, videos, and a list of friends. NoSQL handles that jumble of unstructured data without breaking a sweat.
- IoT applications also benefit. Sensor data coming from thousands of devices can be messy and varied. NoSQL can store it all without trying to force it into a neat little table.
Here's the bottom line: Go with SQL when your data relationships are critical and consistency is king. Choose NoSQL when you need massive scalability and the flexibility to handle diverse, unstructured data.
On-Premise vs. Cloud Hosting
Okay, so you've figured out how to store your data. Now, where will your application actually run? The choice between managing your own physical servers (on-premise) and using a cloud provider is a major fork in the road that impacts your budget, your ability to scale, and your team's workload.
An on-premise setup gives you total control over your hardware and security. The downside? You're responsible for everything. That means buying servers, managing the network, handling all maintenance, and trying to predict future capacity needs. It requires a big upfront investment and a dedicated IT team to keep the lights on.
Cloud hosting, on the other hand, is a pay-as-you-go world. Giants like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure give you access to virtually limitless computing resources on demand.
Let's break down the practical differences:
| Factor | On-Premise Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | High initial capital expenditure (CapEx) | Operational expenditure (OpEx), pay for what you use |
| Scalability | Manual and slow; requires buying new hardware | Automatic and instant; scale up or down in minutes |
| Maintenance | Your team handles all updates, patches, and repairs | The provider manages all hardware and infrastructure |
| Flexibility | Limited to the hardware you've already bought | Access to a vast array of services (AI, machine learning, etc.) |
For most startups and modern businesses, the cloud is the obvious choice. Its flexibility and cost-efficiency are hard to beat. You can launch quickly without a massive initial investment and instantly scale your resources as your user base grows.
If you're still getting your head around this model, our complete guide explains what is cloud hosting and how it can give your business a serious advantage. The freedom to pivot and experiment without being tied down to physical hardware is a game-changer when you're trying to choose a tech stack.
Planning for Security, Scalability, and Maintenance
Picking a tech stack feels like a final move, but it’s really just the opening play. The real test comes months or even years down the road, when the choices you made on day one are pushed to their limits. If you plan for security, scalability, and maintenance from the beginning, you build something that doesn't just launch—it lasts.

This kind of forward-thinking turns your stack from a short-term fix into a long-term asset. It's about building for where you're going, not just for where you are today.
Building a Secure Foundation
Security isn't an add-on you can bolt on later. It has to be baked into the DNA of your tech stack right from the start. A single vulnerability can destroy user trust and cost you a fortune, making proactive security a non-negotiable part of the conversation.
Start by digging into the security reputation of any language or framework you’re considering.
- Active Maintenance: Is the core team actually releasing security patches on a regular basis? An abandoned open-source library is basically a ticking time bomb.
- Built-in Defenses: Look for frameworks that come with protection against common attacks like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and SQL injection. Frameworks like Ruby on Rails and Django have a great track record here.
- Community Vigilance: A big, active community is your best friend. More eyes mean vulnerabilities get found and fixed much faster.
Don't just stop at the core framework, though. Every third-party library or API you plug in is another potential door for attackers. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on web application security best practices.
Designing for Future Growth
What’s the plan for when your user base explodes from a thousand to a million? A tech stack that’s perfect for a scrappy startup might completely fall apart under enterprise-level traffic. Thinking about scalability now saves you from a world of hurt—and expensive migrations—later on.
Scalability usually breaks down into two main types:
- Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up): This is the straightforward approach—just add more horsepower (CPU, RAM) to your existing servers. It’s simple, but you'll eventually hit a wall, and it gets pricey fast.
- Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out): This means adding more machines to your network to spread the workload. It’s more complex to set up but gives you almost endless room to grow.
The architectural patterns you chose earlier make a huge difference here. A monolith is generally tougher to scale horizontally, whereas a microservices architecture is built for it. Your database is just as critical; something like Cassandra is designed for massive horizontal scale, while a traditional SQL database needs a bit more strategic planning.
The goal isn't to over-engineer for a million users on day one. It's to choose a stack that won't stop you from getting there when the time is right.
Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership
The upfront development cost is just the tip of the iceberg. The real number you need to worry about is the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which covers every single expense over the entire life of your application. If you ignore it, you might build something you can't afford to keep running.
TCO includes a lot of hidden or long-term costs that are easy to forget:
- Maintenance and Updates: Your team will spend a surprising amount of time patching security holes, updating libraries, and fixing compatibility issues.
- Hosting and Infrastructure: Cloud hosting bills can spiral out of control as your traffic and data storage grow.
- Talent and Hiring: The availability—and cost—of developers who know your stack will have a direct impact on your budget. Niche technologies often mean smaller talent pools and much higher salaries.
Factoring in these future costs helps you make a smarter financial decision. Sometimes, spending a little more upfront on a well-supported, scalable technology can lead to a dramatically lower TCO down the line, keeping your project healthy for years.
Answering Your Top Tech Stack Questions
Even with a solid plan, choosing a tech stack brings up some nagging, tough questions. These are the "what-ifs" and common hurdles that trip up even experienced teams. Getting straight answers turns abstract ideas into confident decisions.
This section digs into the most common questions we hear from folks trying to nail down their technical foundation. Think of it as a final gut check before you lay the first brick.
How Often Should You Re-Evaluate Your Tech Stack?
A deep-dive re-evaluation every 2-3 years is a good rhythm for most businesses. But that’s not a hard rule. A major business pivot, a merger, or a huge shift in your product roadmap should trigger an immediate review. You don't need a calendar reminder to know when something feels off.
Keep an eye out for these tell-tale signs that it might be time for a change:
- Persistent Performance Issues: Is your team constantly putting out fires? If you’re always fighting performance bottlenecks that simple optimizations can't fix, your stack might be hitting its ceiling.
- Hiring Headaches: It’s a huge red flag when finding developers who know your stack becomes consistently difficult or expensive. That’s a long-term risk you can’t ignore.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Relying on outdated or poorly maintained components is just asking for trouble. It's an open invitation for a security breach.
A review doesn’t always mean a full-blown, terrifying rewrite. More often than not, it’s about making smart upgrades—like swapping out a single component that’s slowing you down or spinning up a new microservice for a demanding feature.
What Is the Biggest Mistake Teams Make?
The single biggest mistake we see is "resume-driven development." This is the classic trap of choosing a technology because it’s new, shiny, and exciting, not because it’s the right tool for the job. The decision gets driven by a developer’s desire to learn something cool, not by what the project actually needs.
This path almost always leads to using unproven, beta-stage tools for critical business functions. The result? A project riddled with obscure bugs, a tiny community to turn to for support, and an even smaller talent pool to hire from.
The best tech stack decisions are almost always boringly practical. They're driven by business goals, project scope, team skills, and budget—never by the latest hype on tech Twitter.
For more on avoiding these pitfalls, check out this practical guide on how to choose a technology stack.
Can You Mix and Match Technologies?
Absolutely. In fact, that's the whole idea behind a microservices architecture. In this setup, different services can be built with completely different tech stacks, each one picked as the best possible tool for its specific job.
For instance, a single complex app might use:
- A Node.js backend for its main API, since it’s fantastic at handling I/O operations.
- A Python service for a machine learning feature that recommends products.
- A real-time chat feature built in Elixir to manage thousands of simultaneous connections.
This "polyglot" approach lets you optimize every single part of your application. The trade-off, however, is a big jump in complexity. You have to think a lot more about deployment, monitoring, and making sure all those different services can talk to each other reliably.
How Does Team Skillset Influence the Choice?
Your team's existing expertise is arguably one of the most important factors here. Sticking with a stack your team already knows inside and out means you'll move faster, make fewer costly mistakes, and spend way less time ramping up.
Learning new tech is great for professional growth, but forcing an unfamiliar, complex stack on your team for a time-sensitive project is a recipe for disaster. If a new technology really is the only path forward, you have to be realistic. Factor in the time and money needed for proper training or for hiring someone with that specific expertise. Your current team is your biggest asset—choose a stack that lets them win.
At Up North Media, we specialize in building custom web applications with scalable, secure, and maintainable tech stacks that align perfectly with your business goals. If you're ready to create a powerful digital foundation for your business, let's talk.
