Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is more than just a buzzword; it's a practical tool for streamlining operations, cutting costs, and freeing up your team for more strategic work. Many business leaders understand the potential of RPA but struggle to visualize how it applies to their specific challenges. This article moves beyond theory to provide concrete robotic process automation examples that businesses are implementing right now.
We will break down seven diverse use cases, from automating tedious invoice processing to streamlining complex supply chain logistics. Each example includes a clear problem statement, an overview of the automated solution, and a breakdown of the tangible benefits achieved. To see a real-world application of automation in finance, consider how one company managed to automate and expand buyer-led financing in a complex market.
Instead of generic success stories, you will find actionable takeaways and implementation insights tailored for small and mid-sized businesses. Our goal is to provide a clear roadmap, helping you identify the most impactful automation opportunities within your own organization. Let's explore how these real-world applications can transform your operational efficiency and drive significant growth.
1. Invoice Processing Automation
Invoice processing is a classic, high-impact use case for robotic process automation, making it a powerful starting point for businesses aiming to streamline their financial operations. This automation involves deploying software "bots" to handle the repetitive, rules-based tasks of managing supplier invoices, from receipt to payment.
RPA bots use Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract key data from various invoice formats, such as invoice number, amount, and line items. The bot then validates this information against purchase orders or existing records in your database, flags discrepancies for human review, and routes compliant invoices through a predefined approval workflow. Once approved, the bot finalizes the process by entering the data into your ERP or accounting system and scheduling the payment. This is one of the clearest robotic process automation examples of how to achieve significant ROI quickly.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Insights
Companies like Coca-Cola have seen remarkable results, reducing their invoice processing time by a staggering 90% using UiPath. Similarly, Siemens automated 85% of their invoice processing with Blue Prism, showcasing the scalability of this solution across large enterprises.
Key Takeaway: The core strategy here is to target a high-volume, error-prone, and time-consuming manual process within a critical business function like finance. Automating invoice processing directly impacts cash flow management, supplier relationships, and employee productivity.
To replicate this success, businesses should follow a phased approach:
- Start Small: Begin by automating invoices from suppliers who use standardized, consistent formats. This builds momentum and allows your team to refine the process before tackling more complex, variable layouts.
- Establish Exception Handling: Design a robust workflow for flagging exceptions, like price mismatches or missing PO numbers. This ensures a human is alerted only when necessary, keeping the automated flow efficient.
- Focus on Change Management: Proactively communicate with your finance team about how their roles will evolve from manual data entry to more strategic tasks like analysis and vendor management.
The following infographic illustrates the simplified, three-step automated workflow.
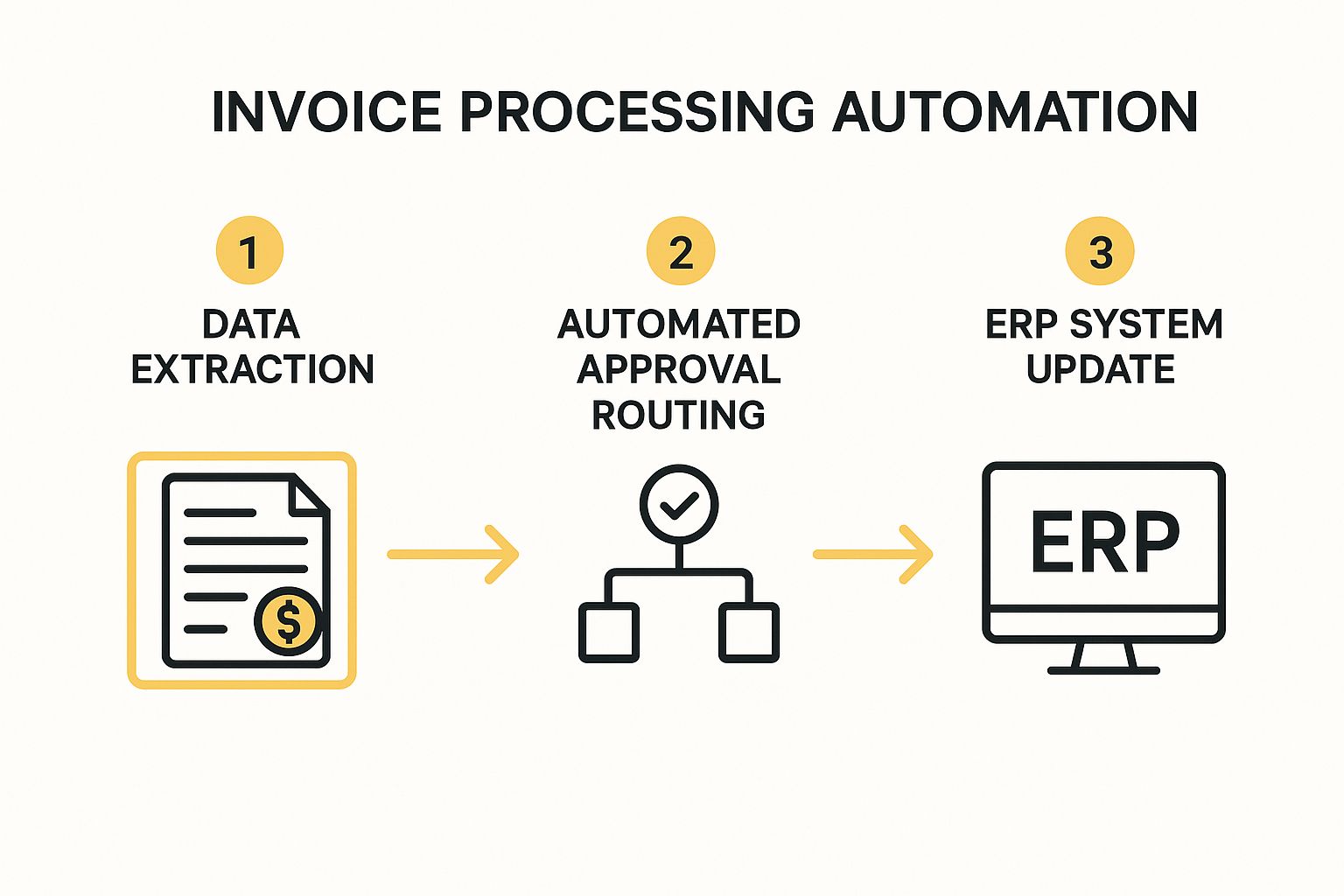
This streamlined flow visualizes how automation transforms a multi-touch, manual process into a highly efficient, hands-off operation. Explore more about the wider impact by reading about the benefits of business process automation.
2. Customer Service Chat Bot Integration
Integrating RPA with customer service chatbots creates a powerful front-line support system, automating routine inquiries and freeing up human agents for more complex, high-value interactions. This involves deploying software bots that can understand customer queries, access multiple backend systems simultaneously, and provide instant, accurate responses or perform simple tasks directly within the chat interface.
These bots can handle common requests like checking an order status, updating account information, or answering frequently asked questions. They integrate with CRMs, ERPs, and knowledge bases to pull relevant data in real-time. This process significantly reduces wait times and offers 24/7 support, making it one of the most customer-facing robotic process automation examples available.

Strategic Analysis & Actionable Insights
Leading companies demonstrate the immense value of this approach. Bank of America's virtual assistant, Erica, has handled over 100 million requests annually, showcasing massive scalability. Similarly, Vodafone's TOBi chatbot successfully resolves 68% of customer queries without human intervention, directly boosting operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Key Takeaway: The strategy is to automate high-volume, low-complexity customer interactions to improve response times and operational costs. This enhances the customer experience while allowing human agents to focus on solving intricate problems that require empathy and critical thinking.
To successfully implement this automation, businesses should consider the following steps:
- Design Clear Escalation Paths: Ensure there is a seamless and clearly communicated process for the bot to transfer a conversation to a human agent when it cannot resolve an issue or detects customer frustration.
- Analyze Conversation Logs: Regularly review chatbot interaction logs to identify common unresolved queries or areas of confusion. Use this data to continuously train and improve the bot's responses and capabilities.
- Implement Sentiment Analysis: Integrate sentiment analysis tools to help the bot recognize negative emotions like frustration or anger, triggering an immediate escalation to a human for a better customer experience.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can transform their customer service from a cost center into an efficient, value-driving operation. Explore how to build and deploy these powerful tools by learning more about customized AI chatbot solutions.
3. Payroll Processing Automation
Payroll processing is an exceptionally high-stakes, repetitive task, making it a prime candidate for automation. It involves deploying RPA bots to manage the entire payroll cycle, from data collection and wage calculation to tax compliance and payment disbursement, ensuring precision and timeliness while drastically reducing manual overhead.

RPA bots automatically gather employee time data from various sources like timesheets or attendance systems. They then calculate gross wages, compute complex deductions for taxes and benefits, and generate individual pay stubs. The bots also handle compliance reporting and initiate direct deposit transactions, transforming a labor-intensive process into a streamlined, automated workflow. This is one of the most compelling robotic process automation examples for HR and finance departments seeking to minimize risk and boost efficiency.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Insights
Global giants have demonstrated the immense value of payroll automation. Unilever successfully automated payroll for 190,000 employees across over 100 countries, while Telefónica cut its payroll processing time by 65% with RPA. In the public sector, an NHS Trust automated its payroll exception handling, saving more than 2,000 hours of manual work each month.
Key Takeaway: The core strategy is to automate a critical, non-discretionary business function where accuracy and compliance are paramount. Automating payroll directly mitigates financial risks, ensures employee satisfaction through timely and accurate payments, and frees up HR professionals for more strategic, value-added activities.
To achieve similar results, businesses should adopt a meticulous approach:
- Prioritize Thorough Testing: Before going live, conduct extensive testing with various scenarios, including overtime, bonuses, and new hires, to ensure the bot handles every calculation correctly.
- Maintain Backup Processes: During the initial deployment phase, keep manual backup procedures in place. This provides a safety net to ensure business continuity and smooths the transition.
- Automate Compliance Updates: Design the automation to be easily updated for changes in tax laws and regulations. Regularly schedule bot maintenance to incorporate these updates and maintain full compliance.
- Implement Comprehensive Logging: Set up detailed logging for every action the bot takes. This creates a transparent, auditable trail that is invaluable for compliance checks and troubleshooting.
4. Data Entry and Migration Automation
Data entry and migration automation is a foundational use case for RPA, addressing one of the most tedious and error-prone areas of business operations. This involves programming software bots to accurately and rapidly transfer large volumes of data between disparate systems, such as from legacy platforms to new cloud-based ERPs, or from spreadsheets and PDFs into a central database.
RPA bots are configured to interact with user interfaces just like a human would, copying data from a source application and pasting it into a target system. They can handle various data formats, perform validation checks, and operate 24/7 without fatigue. This makes them ideal for large-scale system migrations, data consolidation projects, and routine data synchronization tasks. It is a prime example of how robotic process automation examples showcase efficiency gains in back-office functions.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Insights
Success stories in this area are both dramatic and common. MetLife successfully migrated 70 million customer records in just 18 months using RPA, a task that would have taken years with manual effort. Similarly, the Government of Estonia digitized 1.2 million historical documents using RPA, showcasing its power in public sector modernization.
Key Takeaway: The strategy is to eliminate the bottlenecks and human error inherent in manual data handling, especially during critical, one-off projects like system migrations or ongoing, high-volume data transfers. Automating these processes ensures data integrity, accelerates project timelines, and frees up skilled employees for higher-value analytical work.
To achieve similar outcomes, businesses should adopt a structured approach:
- Prioritize Data Quality: Before starting, perform a thorough data quality assessment. Automating the transfer of poor-quality data only accelerates problems. Cleanse and standardize data at the source.
- Implement Robust Validation: Build data validation rules at multiple checkpoints within the bot's workflow. This ensures that only accurate and complete data is entered into the target system, flagging exceptions for review.
- Start with Pilot Projects: Test the automation with small, non-critical data sets first. This allows you to identify and resolve potential issues in the process logic before deploying it at full scale.
This systematic process is a core component of larger digital transformations. You can explore how this fits into a broader strategy by reviewing these workflow automation examples.
5. Email Processing and Response Automation
Automating email processing and responses is a cornerstone of modern operational efficiency, allowing businesses to manage high volumes of communication without overwhelming their support or administrative teams. This automation uses software bots to read, classify, and act on incoming emails based on their content, sender, and keywords.
RPA bots, often enhanced with Natural Language Processing (NLP), can scan an inbox, extract key information like case numbers or customer details, and update corresponding records in a CRM or ticketing system. They can then categorize the message, route it to the correct department, or trigger an automated, templated response for common inquiries. This turns a cluttered inbox into a structured, automated workflow, making it one of the most practical robotic process automation examples for customer-facing teams.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Insights
Financial giant JPMorgan Chase leverages RPA to process over 150,000 customer service emails daily, dramatically improving response times and operational capacity. Likewise, Lufthansa automated 80% of its routine passenger inquiry emails, freeing up agents to handle more complex travel issues and boosting customer satisfaction.
Key Takeaway: The strategy is to target the repetitive, high-volume communication streams that consume significant manual effort. Automating email management directly enhances customer experience through faster responses, reduces the risk of human error, and allows employees to focus on high-value, nuanced conversations.
To achieve similar results, businesses can implement the following tactics:
- Create Comprehensive Classification Rules: Start by defining clear rules to categorize incoming emails (e.g., "Billing Inquiry," "Support Ticket," "Sales Lead"). This forms the logical foundation for all subsequent automated actions.
- Implement Confidence Scoring: For automated responses, use a confidence score system. If the bot is less than 95% certain about the email's intent, it should automatically escalate the message to a human agent to prevent incorrect replies.
- Set Up Clear Escalation Paths: Design a seamless workflow for emails requiring human intervention. The bot should not just flag the email but also enrich it with customer history or relevant data before passing it to the appropriate team member.
6. Financial Reconciliation Automation
Financial reconciliation is a fundamental accounting process that is often manual, repetitive, and highly susceptible to human error. Automation in this area involves deploying RPA bots to compare and match financial records across different systems, such as bank statements, general ledgers, and sub-ledgers, ensuring they are in agreement. This is a critical function for maintaining financial integrity and regulatory compliance.
RPA bots are configured to access multiple systems, retrieve transactional data, and apply predefined matching rules. They can automatically identify and clear matching entries, flag discrepancies like unmatched amounts or missing transactions, and generate comprehensive reconciliation reports. This provides one of the most compelling robotic process automation examples for finance departments, freeing up accountants from tedious validation tasks to focus on investigating and resolving complex exceptions.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Insights
Leading financial institutions and global corporations have achieved significant gains in this area. HSBC, for example, successfully automated 95% of its nostro reconciliation processes, drastically reducing manual effort. Similarly, General Electric leveraged RPA to cut its monthly closing time from eight days down to just two, while Deutsche Bank automated foreign exchange reconciliation to process over one million transactions daily.
Key Takeaway: The core strategy is to automate a time-sensitive, high-volume process that is foundational to financial reporting and compliance. Automating reconciliation directly improves the accuracy of financial statements, accelerates financial closing cycles, and enhances the audit trail.
To replicate this success, organizations should adopt a measured approach:
- Start with Simpler Processes: Begin by automating straightforward reconciliations, such as bank-to-book or low-volume intercompany accounts. This allows your team to learn the technology and build confidence before tackling more complex areas.
- Establish Clear Business Rules: Define precise matching logic and tolerance levels (e.g., acceptable variance amounts) for the bots to follow. Clear rules are essential for minimizing false exceptions and maximizing automation rates.
- Implement Robust Exception Handling: Design a clear and efficient workflow for routing discrepancies to the appropriate human expert. The goal is not to eliminate human involvement but to ensure they only intervene when their expertise is truly needed.
7. Supply Chain Management Automation
Automating supply chain management with RPA is a transformative strategy for businesses aiming to build resilience and efficiency in their logistics and procurement operations. This application involves deploying software bots to orchestrate a series of complex, interconnected tasks, such as order processing, inventory monitoring, shipment tracking, and supplier communications.
RPA bots act as the digital glue between disparate systems, including ERPs, supplier portals, and logistics platforms. They can automatically process incoming orders, update inventory levels in real-time, track shipments across carrier websites, and send automated status updates to stakeholders. By handling these repetitive, high-volume tasks, bots ensure data accuracy, reduce lead times, and free up human teams to manage exceptions and strategic supplier relationships. This is a powerful robotic process automation example for optimizing the entire value chain.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Insights
Retail giant Walmart automated its supplier onboarding process, cutting processing time by an impressive 75%. Similarly, Nestlé automated procurement processes across more than 150 countries, generating over $50 million in annual savings and demonstrating the global scale and financial impact of supply chain RPA.
Key Takeaway: The core strategy is to target the repetitive, data-intensive touchpoints that create bottlenecks and introduce errors in the supply chain. Automating these processes directly enhances operational visibility, reduces costs, and improves responsiveness to market changes.
To achieve similar success, businesses should implement a structured plan:
- Map the End-to-End Process: Before deploying bots, create a detailed map of all supply chain touchpoints, from procurement to final delivery. This identifies the best opportunities for automation and reveals potential dependencies.
- Standardize Communication: Establish standardized protocols and templates for supplier communications, such as purchase orders and status requests. This makes it easier for bots to parse information and execute tasks consistently.
- Implement Real-Time Monitoring: Deploy bots to continuously monitor inventory levels and shipment statuses, and configure real-time alerts for stakeholders when predefined thresholds are met or disruptions occur. This proactive approach prevents stockouts and delays.
7 Key Automation Use Cases Compared
| Automation Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invoice Processing Automation | Moderate to High – handling multiple invoice formats and exception workflows | Requires OCR tech and ERP integration | Reduces processing time by up to 90%, improves accuracy and compliance | Finance departments processing high invoice volumes | High accuracy, faster payments, real-time visibility |
| Customer Service Chat Bot Integration | Moderate – multi-system integration with NLP and continuous training | Needs NLP, CRM/billing integration, ongoing optimization | Significantly reduces response time, supports 24/7 customer service | Customer service departments handling routine inquiries | Consistent quality, supports volume, frees agents for complex issues |
| Payroll Processing Automation | Moderate to High – complex tax rules setup and system integration | Integration with HR/time tracking and tax systems | Eliminates errors, ensures compliance, reduces payroll time | HR and payroll teams managing large employee bases | Accurate payroll, compliance, scalable |
| Data Entry and Migration Automation | Moderate – data validation, error handling needed for clean migration | Multi-format data extraction tools, error handling | Processes large volumes quickly, reduces manual entry errors | Data migration, consolidation, routine transfers | Fast, error reduction, continuous operation |
| Email Processing and Response Automation | Moderate – NLP classification and template maintenance | NLP, template creation, CRM/ticketing systems | Ensures consistent responses, 24/7 email handling | Customer support email management | No missed emails, faster responses, routing automation |
| Financial Reconciliation Automation | High – complex accounting rules and integration with multiple systems | Requires accounting expertise and multiple financial integrations | Improves accuracy, reduces month-end closing time | Finance teams for transaction matching and audits | Real-time reconciliation, audit trails, accuracy |
| Supply Chain Management Automation | High – complex multi-system integration and supplier variability | ERP, supplier portals, logistics integration | Reduces costs, improves supplier management, accelerates processing | Supply chain logistics and procurement | End-to-end visibility, cost reduction, faster cycles |
From Examples to Execution: Your Next Steps in Automation
The diverse array of robotic process automation examples we've explored, from streamlining invoice processing to automating complex supply chain logistics, reveals a powerful, unifying truth: RPA is not a futuristic concept, but a present-day strategic imperative. The detailed breakdowns of each use case, whether in payroll, customer service, or data migration, demonstrate that success hinges less on the technology itself and more on the strategic vision behind its deployment.
By moving beyond simple task replacement, businesses unlock the true potential of automation. The key is to view RPA not as a cost-cutting tool alone, but as a catalyst for operational excellence, enhanced data accuracy, and superior customer experiences. Each example shared a common thread: identifying high-volume, rule-based processes that, when automated, freed human teams to focus on high-value, strategic work that drives growth and innovation.
Key Takeaways for Your Automation Journey
As you consider implementing RPA, remember these core principles distilled from the successful examples:
- Start Small, Scale Smart: The most effective automation initiatives begin with a well-defined pilot project. Choose a single, high-impact process like data entry or financial reconciliation to prove the concept, measure ROI, and build internal momentum before tackling more complex workflows.
- Process Purity is Paramount: Automation cannot fix a broken process. Before deploying a single bot, meticulously map, analyze, and optimize the existing workflow. A streamlined manual process is the ideal foundation for a highly efficient automated one.
- Focus on the Human Element: The goal is augmentation, not just replacement. Frame your RPA strategy around empowering your employees. By automating tedious, repetitive tasks, you enable your team to apply their critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills to more significant challenges.
Your Actionable Next Steps
Translating these insights into action is the crucial next phase. The journey from seeing robotic process automation examples to executing a successful strategy requires a clear, methodical approach.
- Identify Prime Candidates: Convene a team of department leaders to brainstorm and list repetitive, rule-based tasks across your organization. Use the examples in this article, like email processing or payroll, as a guide to spot similar opportunities within your own operations.
- Quantify the Opportunity: For your top one or two candidates, calculate the potential ROI. Estimate the hours saved, the reduction in error rates, and the potential for faster service delivery. This business case will be essential for securing buy-in and resources.
- Develop a Pilot Project Scope: Define the precise start and end points of the process you will automate. Document every step, rule, and exception. This detailed documentation is the blueprint your development partner or internal team will use to build the bot.
Ultimately, mastering RPA is about building a more resilient, efficient, and intelligent organization. By strategically applying automation, you create a system where operational drag is minimized, and human potential is maximized. This shift allows your business to become more agile, responsive to market changes, and better equipped to serve your customers. The examples prove that any business, regardless of size or industry, can harness this technology to build a significant competitive advantage.
Ready to turn these examples into a reality for your business? The experts at Up North Media specialize in developing custom AI and automation solutions that streamline operations and drive tangible results. Visit Up North Media to learn how we can design and implement an RPA strategy tailored to your unique business needs.
